INDIAN FOOD PROCESSING INDUSTRY 
| Size of the INDUSTRY |
|
| Geographical distribution | Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Gujarat, Hyderabad, Pune, all the major cities in the country |
| Output per annum | The Indian food industry sales turnover is Rs 140,000 crore annually as at the start of year 2000. |
| Percentage in world market | The value of the Indian food industry has increased from Rs. 3.09 trillion in 1993-94 to Rs. 3.99 trillion in 2000-01. |
| Market capitalization | The country’s GDP growth rate had increase from 3.5 % in 2002-03 to 9 % in 2006-07 |
The Indian agriculture sector has come a long way since the time of independence. With the emergence of green revolution, India agricultural Industries have transformed itself from a country of shortages to a land of surpluses. With the rapid growth of the Indian economy, a shift is also being seen in the consumption pattern of the country, from cereals to more varied and nutritious diet of fruit and vegetables, milk, fish, meat and poultry products. All these efforts have resulted in the development of a sunrise industry namely the Food Processing Industries.

India is the nation of over 1.10 billion consumers, there is a large untapped domestic market of 1,000 million consumers in the food processing sector and 200 million more consumers are expected to shift to processed food by the end of the year 2010. India is analyzed as the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world. Although there is a huge wastage of perishable food items in the country due to lack of proper food processing facilities and the level of processing is only about 2.2 %. However, Indian Food processing Industry has got tremendous potential to unleash large scale process based on farm activities to exploit the emerging global business opportunities.
In July 1988, The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MFPI) was set up to give an impetus to development of food processing sector in India. The Ministry formulates and implements the policies & plans for the food processing industries according to the overall national priorities and objectives. It acts as a catalyst for bringing in greater investment into the sector while guiding and helping the industry and even creating a conducive environment for healthy growth of the food processing industry.
Indian Food Processing Industry covers fruit and vegetables; meat and poultry; milk and milk products, alcoholic beverages, fisheries, plantation, grain processing, consumer products groups like confectionery, chocolates and cocoa products, Soya-based products, mineral water, high protein foods, etc. The most promising sub-sectors consists of Soft-drink bottling, Confectionery manufacture, Fishing, aquaculture, Grain-milling and grain-based products, Meat and poultry processing, Tomato paste, Fast-food, Ready-to-eat breakfast cereals, Food additives, flavors etc.
Indian Food Processing Industry is the world’s second largest producer of food next to China and has the potential of being the biggest in the food and agricultural sector. The total food production in India is likely to double in the next ten years and there is an opportunity for large investments in food and food processing technologies, skills and equipment, especially in areas of Canning, Dairy and Food Processing, Specialty Processing, Packaging, Frozen Food/Refrigeration and Thermo Processing. Fruits & Vegetables, Fisheries, Milk & Milk Products, Meat & Poultry, Packaged/Convenience Foods, Alcoholic Beverages & Soft Drinks and Grains are important sub-sectors of the food processing industry. Health food and health food supplements is another rapidly rising segment of this industry which is gaining vast popularity amongst the health conscious.

Over the past three and half decades the Indian agricultural and dairy sectors have achieved remarkable successes. Besides India being one of the world’s largest producers of food-grains, India has been ranked second in the world for the production of fruits and vegetables and regarded first in milk production providing much needed food security to the nation.
The accomplishments and achievements of the green and white revolutions have contributed to the development of Indian Food Processing Industry.
India’s Increased urbanization, improved standards of living and the convenient need of dual income families point out to the major market potentialities in the food processing and marketing sectors. There is also evidence that from the presence of several global foods giants and leading Indian industrial enterprises in the country’s food processing sector such as: Nestle India Ltd, Cadbury’s India Ltd, Kelloggs India, Hindustan Lever Ltd, ITC-Agro, Godrej Foods and MTR Foods Ltd. In the present world of globalized milieu, the surplus food production, as well as the increasing preference for Indian foods needs to be leveraged to achieve economic and strategic objectives through exports.
Further there was an absolute revenue increase of Rs. 900 billion in food manufacturing between 1993 and 2000 which is in contrast with Rs. 150 billion and Rs. 300 billion for the pharmaceutical and IT industries, respectively. Overall, taking everything in accordance the value of the Indian food industry has increased from Rs. 3.09 trillion in 1993-94 to Rs. 3.99 trillion in 2000-01. The segments which have the largest growth potential have been identified as dairy, wheat, fruits and vegetables, and poultry. This report has also identified some of the major challenges for the emerging food industry in India.
The Indian Food Processing Industry with its vast potential has emerged as one of the major driver of economic growth and development. It is encouraging to make analyses that while the country’s GDP growth rate had increase from 3.5 % in 2002-03 to 9 % in 2006-07, the Food Processing Industry has grown from 7 % to 13.1 % during the same period.
In 2014, the Exports of agricultural products from India are expected to cross around US$ 22 billion mark and would account for 5 % of the world’s agriculture exports, Even the Exports of floriculture, fresh fruits and vegetables, processed fruits and vegetables, animal products, other processed foods and cereals rose to US$ 7891.8 million in 2008-09 from US$ 7877.07 million in 2007-08, according to the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA).
Moreover, Indian Food Processing Industry has exported schedule products, floriculture and seeds, fruits and vegetables, processed fruits and vegetables, livestock products, other processed foods and cereals worth US$ 6.53 billion from 2009-2010, according to APEDA.
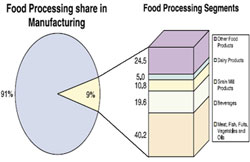 |
India has been and is one of the world’s major food producers but accounts for less than 1.5 % of international food trade. This indicates vast scope for both investors and exporters. In 1998, Indian Food exports stood at US $5.8 billion whereas the world total was US $438 billion. The Indian food industries sales turnover is Rs 140,000 crore annually as at the start of year 2000. The industry has the highest number of plants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) outside the USA.
|
- ITC Limited
- Parle Products Pvt. Ltd.
- Agro Tech Foods
- Amul
- Perfetti India Ltd.
- Cadbury India Ltd.
- PepsiCo India Holdings
- Nestle India Pvt. Ltd.
- Britannia Industries Ltd.
- Hindustan Lever Limited
- Milkfood
- MTR Foods Limited
- Godrej Industries Limited
- Gits Food Products Pvt. Ltd.
- Dabur India Ltd.
- Unilever
- Conagra Foods
- Nissin Foods
- Walmart
- Venky’s
Food processing is a branch of food science, which exists from the prehistoric times. Food processing has certain methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into food for the consumption of humans and animals.
For job opportunities in Indian Food Processing Industry the candidates should usually have a degree in B.Sc. in Home Science/ Food Technology/ Food Science, one should have passed 10+2 examinations with Physics, Chemistry and Biology as the main subjects. For M.Sc / Management, the minimum eligibility is a B.Sc. There are opportunities like Food technologists, technicians, bio technologists and engineers which are required in this industry for the practical application of the principles of many disciplines of science in the manufacturing or production, preservation and packaging, processing and canning of various food products.
- Food technologists: They have been given the responsibility of determining whether a particular process is being performed in a certain specified way or not in the Food processing sector.
- Organic Chemists: They advise on the various methods by which the raw materials have to be converted into processed food.
- Biochemists: They usually support and suggest improvements in flavor, texture, storage and quality.
- Analytical Chemists: They analyze food products to maintain quality and healthy factor.
- Home Economists: They are in a way expert for nutrition. They even test the food and recipes according to the directions on the containers.
- Engineers: Candidates in the field of Chemical, Mechanical, Industrial, Electrical, Agricultural and Civil engineers are all required for planning, designing, improving and maintaining the processing systems in the food processing Sector.
- Research Scientists: They take up the task of performing the experiments regarding improvement in yield, flavor, nutritive value and general acceptability of the packaged food.
- Managers and accountants managers and accountants are required for administration and the finances apart from supervising the processing work.
India’s Position in World’s Production
- Largest producer of milk in the world -105 million tonnes per annum.
- India is the largest in the livestock population with about 485 million tones per annum.
- It is second largest producer of fruits & vegetables which accounts for 150 million tonnes per annum.
- India is the third largest producer of food grain accounting for 230 million tonnes per annum.
- Third largest producer of fish – 7 million tonnes per annum
- India has 52% cultivable land compared to 11% world average and 15 major climates in the world exist in India, there 46 out of 60 soil types exist in India and 20 agri-climatic regions.